
A40 - Steel coils for laser cutting applications
These steels are particularly suitable for manufacturing complex parts or for improving productivity when parts are to be produced on a small scale.
 Download
Download
Available grades:
High yield strength steels for cold forming
Structural steels
Properties
Steel coils for laser cutting applications (CLAS) are hot rolled coils produced in specific grades, developed for applications using computer-controlled thermal and mechanical cutting equipment (laser, plasma etc).
Two ranges are available: structural and high yield strength steels for cold forming.
- The structural steel range begins with S200 CLAS AM FCE grade, which combines the drawability of DD12 AM FCE (EN 10111:2008) and a narrow tolerance range for the mechanical properties. All the other grades are improved structural steels in compliance with EN 10025-2:2004.
- The range of high yield strength steels for cold forming comprises improved versions of Amstrong® 315MC, Amstrong® 355MC, Amstrong® 420MC and Amstrong® 500MC, as per EN 10149-2:2013.
All these grades are designed to:
- Give improved productivity, quality and consistency with laser cutting
- Meet the most stringent flatness requirements after cutting
Advantages
Steel coils supplied for laser cutting are virtually free of internal stresses and can therefore be used to produce sheets with guaranteed flatness before, during and after cutting, provided that appropriate decoiling tools and procedures are used. Sheets produced on cutting-to-length lines certified by ArcelorMittal may have guaranteed flatness before, during and after cutting (see data sheet A42).
For thicknesses below 16 mm, steels for laser cutting offer significantly higher laser cutting speeds than those obtained with standard grades and/or conventional cutting processes (plasma, oxy-cutting).
These steels can be hot dip galvanised.
Applications
These grades are particularly suitable for manufacturing complex parts or for improving productivity when parts are to be produced on a small scale.
Since 1 July 2013, the Construction Products Regulation (Regulation (EU) No. 305/2011 – CPR) has required that CE marking be affixed to all products delivered in accordance with a harmonised standard (e.g. EN 10025). This CE marking guarantees, for the uses defined in the standard, the properties described in the declaration of performance submitted by the manufacturer.
The S235 CLAS AM FCE, S275 CLAS AM FCE and S355 CLAS AM FCE steels in this data sheet comply with this Regulation.
Surface quality
Laser cutting speed largely depends on surface homogeneity and reflectivity. To improve productivity for our clients, ArcelorMittal has developed several surface finishes compatible with laser cutting:
- Mill finish:
- Surface appearance: only A (unexposed) is available
- Surface cleanliness: on request, Amstrong® grades can be delivered with an improved surface finish on black hot rolled product. Contact our commercial teams for further information.
- Pickled:
ArcelorMittal's hydrochloric acid pickling process produces a clean, more favourable surface for laser cutting than that produced by sulphuric acid pickling.
- Surface appearance: A (unexposed) and B (exposed) are available
- Protection:
- Protective oil may be applied
- Easyfilm® HPE is available. It offers more uniform dry surface protection than oil and favourably reduces the reflectivity of the steel. Moreover, since no oil is used, workplace floors are cleaner and safer.
For more information, see data sheet A80.
Weldability
Due to their low carbon equivalent value (see table of chemical properties), ArcelorMittal's steel coils for laser cutting applications offer excellent weldability.
Brand correspondence
High yield strength steels for cold forming
Full table
| |
EN 10025-2:2004 |
EN 10149-2:2013 |
EN 10111:2008 |
Old brand names |
| Amstrong® 320MC CLAS AM FCE |
|
S315MC |
|
|
| Amstrong® 360MC CLAS AM FCE |
|
S355MC |
|
Sollaser® 380/Sidlaser® 380/Superlaser 355MC |
| Amstrong® 420MC CLAS AM FCE |
|
S420MC |
|
Sollaser® 440/Sidlaser® 420 |
| Amstrong® 500MC CLAS AM FCE |
|
S500MC |
|
|
Amstrong® 320MC CLAS AM FCE
| |
Amstrong® 320MC CLAS AM FCE |
| EN 10025-2:2004 |
|
| EN 10149-2:2013 |
S315MC |
| EN 10111:2008 |
|
| Old brand names |
|
Amstrong® 360MC CLAS AM FCE
| |
Amstrong® 360MC CLAS AM FCE |
| EN 10025-2:2004 |
|
| EN 10149-2:2013 |
S355MC |
| EN 10111:2008 |
|
| Old brand names |
Sollaser® 380/Sidlaser® 380/Superlaser 355MC |
Amstrong® 420MC CLAS AM FCE
| |
Amstrong® 420MC CLAS AM FCE |
| EN 10025-2:2004 |
|
| EN 10149-2:2013 |
S420MC |
| EN 10111:2008 |
|
| Old brand names |
Sollaser® 440/Sidlaser® 420 |
Amstrong® 500MC CLAS AM FCE
| |
Amstrong® 500MC CLAS AM FCE |
| EN 10025-2:2004 |
|
| EN 10149-2:2013 |
S500MC |
| EN 10111:2008 |
|
| Old brand names |
|
Prev grade
Next grade
Structural steels
Full table
| |
EN 10025-2:2004 |
EN 10149-2:2013 |
EN 10111:2008 |
Old brand names |
| S200 CLAS AM FCE |
|
|
DD12 |
Sollaser® 220/Sidlaser® 220/Superlaser DD12 |
| S240 CLAS AM FCE |
S235J0 |
|
|
Sollaser® 260/Sidlaser® 240/Superlaser 235 |
| S275 CLAS AM FCE |
S275J0 |
|
|
|
| S355 CLAS AM FCE |
S355J0 |
|
|
|
S200 CLAS AM FCE
| |
S200 CLAS AM FCE |
| EN 10025-2:2004 |
|
| EN 10149-2:2013 |
|
| EN 10111:2008 |
DD12 |
| Old brand names |
Sollaser® 220/Sidlaser® 220/Superlaser DD12 |
S240 CLAS AM FCE
| |
S240 CLAS AM FCE |
| EN 10025-2:2004 |
S235J0 |
| EN 10149-2:2013 |
|
| EN 10111:2008 |
|
| Old brand names |
Sollaser® 260/Sidlaser® 240/Superlaser 235 |
S275 CLAS AM FCE
| |
S275 CLAS AM FCE |
| EN 10025-2:2004 |
S275J0 |
| EN 10149-2:2013 |
|
| EN 10111:2008 |
|
| Old brand names |
|
S355 CLAS AM FCE
| |
S355 CLAS AM FCE |
| EN 10025-2:2004 |
S355J0 |
| EN 10149-2:2013 |
|
| EN 10111:2008 |
|
| Old brand names |
|
Prev grade
Next grade
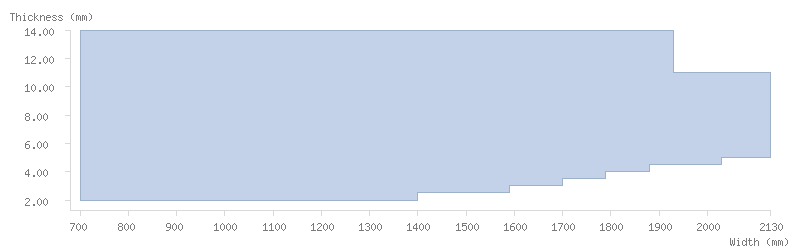
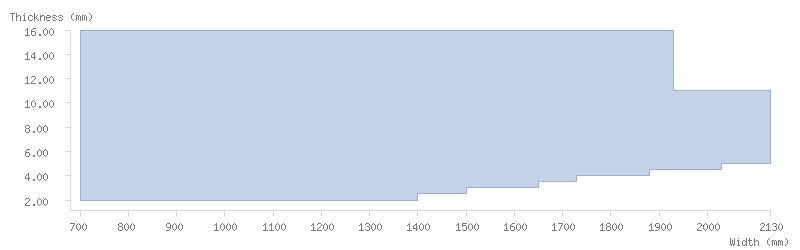
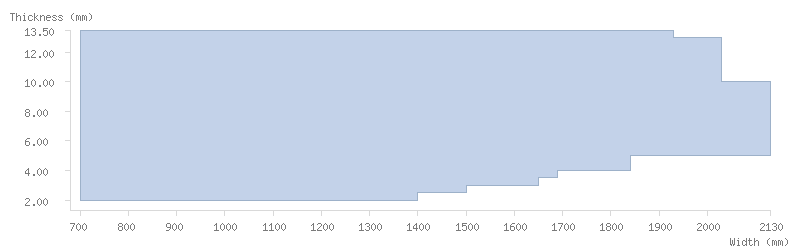
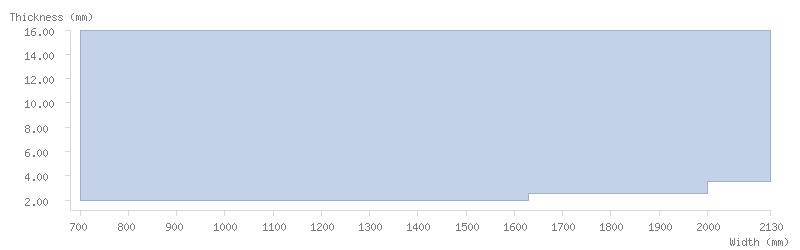
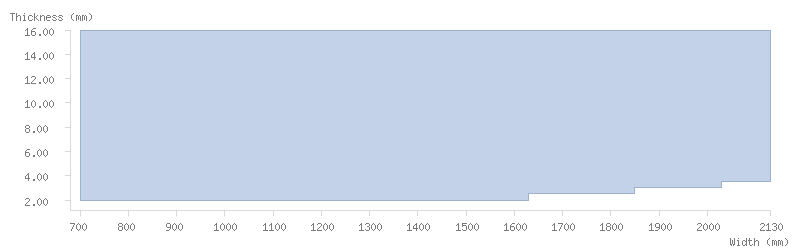
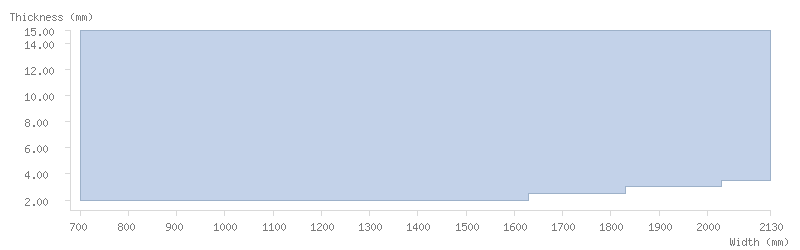
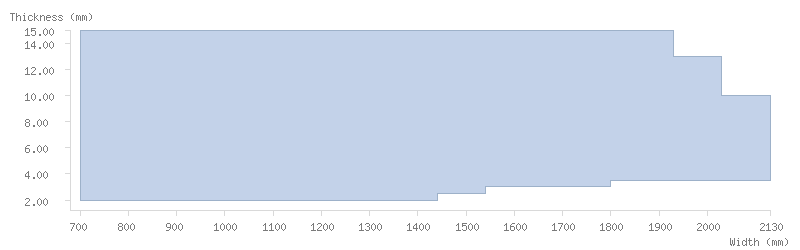
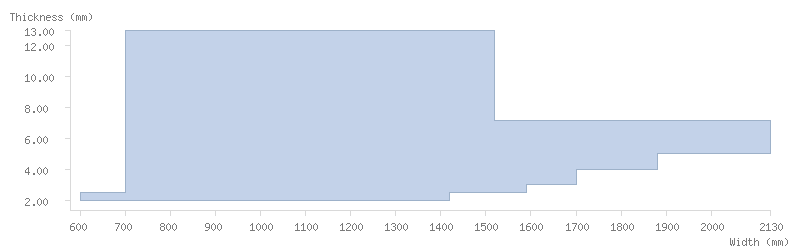
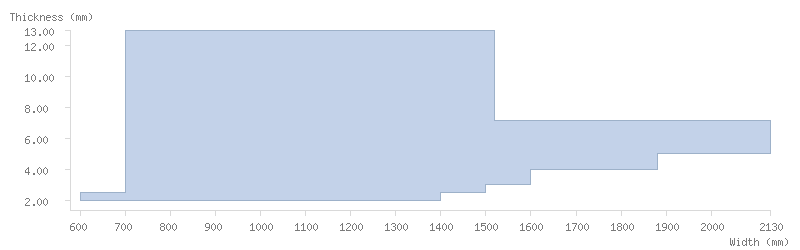
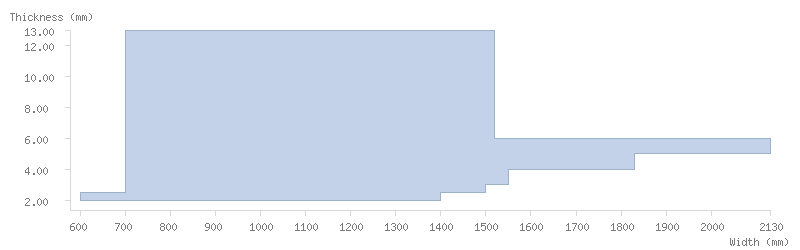
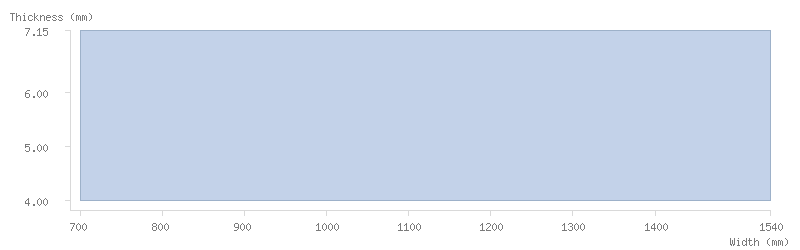
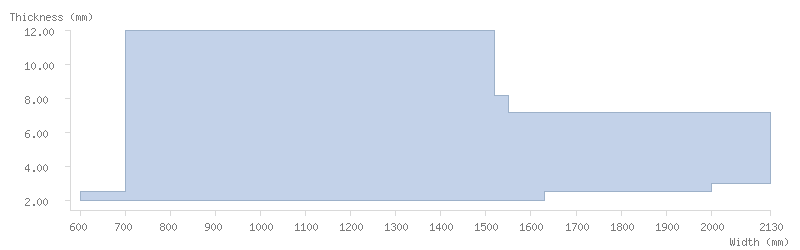
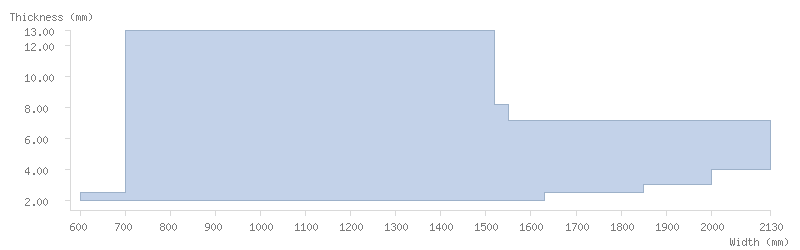
Dimensions
Thickness tolerance
The consistent thickness and reduced internal stresses of these coils make it possible to operate laser cutting machines continuously by lowering the breakdown risk and the frequency of laser cutting head breakage. This allows the use of fully automated loading and discharging systems.
The following thickness tolerances (EN 10051:2010) are available: 3/4, 1/2 and 1/3 for both mill finish and pickled steels. Contact our commercial teams for stricter tolerances.
Amstrong® grades are delivered with a thickness tolerance of 1/2 EN if a tighter tolerance is not requested.
Flatness tolerance
Since the degree of sheet flatness obtained mainly depends on the uncoiling and levelling process used during laser cutting, we cannot offer any guarantee for coil products supplied.
Dimension tables
The following tables show the dimensions available for ArcelorMittal's coils:
Mill finish
Pickled coils
Mechanical properties
High yield strength steels for cold forming
Full table
| |
Direction |
Thickness (mm) |
Re (MPa) |
Rm (MPa) |
A80 (%) |
A 5.65√So (%) |
Bending ratio (th) |
KV -20°C (J) |
| Amstrong® 320MC CLAS AM FCE |
L |
2 - 3 |
320 - 420 |
420 - 500 |
≥ 22 |
≥ 27 |
- |
- |
| 3 - 6 |
- |
| 6 - 14 |
≥ 40 |
| T |
2 - 3 |
345 - 450 |
435 - 540 |
≥ 21 |
≥ 26 |
≥ 0 |
- |
| 3 - 14 |
- |
| Amstrong® 360MC CLAS AM FCE |
L |
2 - 3 |
360 - 440 |
450 - 530 |
≥ 21 |
- |
- |
- |
| 3 - 6 |
- |
≥ 26 |
| 6 - 16 |
≥ 40 |
| T |
2 - 3 |
380 - 460 |
460 - 540 |
≥ 20 |
- |
≥ 0 |
- |
| 3 - 16 |
- |
≥ 25 |
| Amstrong® 420MC CLAS AM FCE |
L |
2 - 3 |
420 - 500 |
490 - 590 |
≥ 18 |
- |
- |
- |
| 3 - 6 |
- |
≥ 23 |
| 6 - 14 |
≥ 40 |
| T |
2 - 3 |
440 - 520 |
500 - 600 |
≥ 17 |
- |
≥ 0.5 |
- |
| 3 - 14 |
- |
≥ 22 |
| Amstrong® 500MC CLAS AM FCE |
L |
< 2 |
500 - 600 |
570 - 700 |
≥ 15 |
- |
- |
- |
| 2 - 3 |
≥ 16 |
| 3 - 6 |
- |
≥ 19 |
| 6 - 10 |
≥ 40 |
| T |
< 2 |
530 - 630 |
570 - 700 |
≥ 14 |
- |
≥ 0.6 |
- |
| 2 - 3 |
≥ 15 |
| 3 - 6 |
- |
≥ 18 |
| 6 - 10 |
≥ 1 |
Bending ratio is as defined in EN 10149-2:2013: “Bending at 180° minimum mandrel diameter”.
Amstrong® 320MC CLAS AM FCE
| |
Direction |
Thickness (mm) |
Amstrong® 320MC CLAS AM FCE |
| Re (MPa) |
L |
2 - 14 |
320 - 420 |
| T |
2 - 14 |
345 - 450 |
| Rm (MPa) |
L |
2 - 14 |
420 - 500 |
| T |
2 - 14 |
435 - 540 |
| A80 (%) |
L |
2 - 3 |
≥ 22 |
| T |
2 - 3 |
≥ 21 |
| A 5.65√So (%) |
L |
2 - 14 |
≥ 27 |
| T |
2 - 14 |
≥ 26 |
| Bending ratio (th) |
T |
2 - 14 |
≥ 0 |
| KV -20°C (J) |
L |
6 - 14 |
≥ 40 |
Amstrong® 360MC CLAS AM FCE
| |
Direction |
Thickness (mm) |
Amstrong® 360MC CLAS AM FCE |
| Re (MPa) |
L |
2 - 16 |
360 - 440 |
| T |
2 - 16 |
380 - 460 |
| Rm (MPa) |
L |
2 - 16 |
450 - 530 |
| T |
2 - 16 |
460 - 540 |
| A80 (%) |
L |
2 - 3 |
≥ 21 |
| T |
2 - 3 |
≥ 20 |
| A 5.65√So (%) |
L |
3 - 16 |
≥ 26 |
| T |
3 - 16 |
≥ 25 |
| Bending ratio (th) |
T |
2 - 16 |
≥ 0 |
| KV -20°C (J) |
L |
6 - 16 |
≥ 40 |
Amstrong® 420MC CLAS AM FCE
| |
Direction |
Thickness (mm) |
Amstrong® 420MC CLAS AM FCE |
| Re (MPa) |
L |
2 - 14 |
420 - 500 |
| T |
2 - 14 |
440 - 520 |
| Rm (MPa) |
L |
2 - 14 |
490 - 590 |
| T |
2 - 14 |
500 - 600 |
| A80 (%) |
L |
2 - 3 |
≥ 18 |
| T |
2 - 3 |
≥ 17 |
| A 5.65√So (%) |
L |
3 - 14 |
≥ 23 |
| T |
3 - 14 |
≥ 22 |
| Bending ratio (th) |
T |
2 - 14 |
≥ 0.5 |
| KV -20°C (J) |
L |
6 - 14 |
≥ 40 |
Amstrong® 500MC CLAS AM FCE
| |
Direction |
Thickness (mm) |
Amstrong® 500MC CLAS AM FCE |
| Re (MPa) |
L |
< 10 |
500 - 600 |
| T |
< 10 |
530 - 630 |
| Rm (MPa) |
L |
< 10 |
570 - 700 |
| T |
< 10 |
570 - 700 |
| A80 (%) |
L |
< 2 |
≥ 15 |
| 2 - 3 |
≥ 16 |
| T |
< 2 |
≥ 14 |
| 2 - 3 |
≥ 15 |
| A 5.65√So (%) |
L |
3 - 10 |
≥ 19 |
| T |
3 - 10 |
≥ 18 |
| Bending ratio (th) |
T |
< 6 |
≥ 0.6 |
| 6 - 10 |
≥ 1 |
| KV -20°C (J) |
L |
6 - 10 |
≥ 40 |
Prev grade
Next grade
Bending ratio is as defined in EN 10149-2:2013: “Bending at 180° minimum mandrel diameter”.
Structural steels
Full table
| |
Direction |
Thickness (mm) |
Re (MPa) |
Rm (MPa) |
A80 (%) |
A 5.65√So (%) |
Bending ratio (th) |
KV 0°C (J) |
| S200 CLAS AM FCE |
T |
2 - 3 |
200 - 310 |
320 - 410 |
≥ 27 |
- |
- |
- |
| 3 - 16 |
200 - 300 |
320 - 400 |
- |
≥ 32 |
| S240 CLAS AM FCE |
L |
6 - 16 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
≥ 27 |
| T |
2 - 3 |
240 - 320 |
360 - 440 |
≥ 22 |
- |
- |
- |
| 3 - 16 |
- |
- |
- |
≥ 28 |
| S275 CLAS AM FCE |
L |
6 - 16 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
≥ 27 |
| T |
2 - 2.5 |
≥ 275 |
430 - 580 |
< 16 |
- |
- |
- |
| 2.5 - 3 |
< 17 |
| 3 - 16 |
410 - 560 |
- |
< 21 |
| S355 CLAS AM FCE |
L |
6 - 16 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
≥ 27 |
| T |
2 - 2.5 |
≥ 355 |
510 - 610 |
≥ 15 |
- |
≥ 1 |
- |
| 2.5 - 3 |
≥ 16 |
| 3 - 16 |
490 - 590 |
- |
≥ 20 |
Bending ratio: the values of the bending radius are applicable for bend angles ≤ 90º, as proposed in EN 10025-2:2004.
S200 CLAS AM FCE
| |
Direction |
Thickness (mm) |
S200 CLAS AM FCE |
| Re (MPa) |
T |
2 - 3 |
200 - 310 |
| 3 - 16 |
200 - 300 |
| Rm (MPa) |
T |
2 - 3 |
320 - 410 |
| 3 - 16 |
320 - 400 |
| A80 (%) |
T |
2 - 3 |
≥ 27 |
| A 5.65√So (%) |
T |
3 - 16 |
≥ 32 |
S240 CLAS AM FCE
| |
Direction |
Thickness (mm) |
S240 CLAS AM FCE |
| Re (MPa) |
T |
2 - 3 |
240 - 320 |
| Rm (MPa) |
T |
2 - 3 |
360 - 440 |
| A80 (%) |
T |
2 - 3 |
≥ 22 |
| A 5.65√So (%) |
T |
3 - 16 |
≥ 28 |
| KV 0°C (J) |
L |
6 - 16 |
≥ 27 |
S275 CLAS AM FCE
| |
Direction |
Thickness (mm) |
S275 CLAS AM FCE |
| Re (MPa) |
T |
2 - 16 |
≥ 275 |
| Rm (MPa) |
T |
2 - 3 |
430 - 580 |
| 3 - 16 |
410 - 560 |
| A80 (%) |
T |
2 - 2.5 |
< 16 |
| 2.5 - 3 |
< 17 |
| A 5.65√So (%) |
T |
3 - 16 |
< 21 |
| KV 0°C (J) |
L |
6 - 16 |
≥ 27 |
S355 CLAS AM FCE
| |
Direction |
Thickness (mm) |
S355 CLAS AM FCE |
| Re (MPa) |
T |
2 - 16 |
≥ 355 |
| Rm (MPa) |
T |
2 - 3 |
510 - 610 |
| 3 - 16 |
490 - 590 |
| A80 (%) |
T |
2 - 2.5 |
≥ 15 |
| 2.5 - 3 |
≥ 16 |
| A 5.65√So (%) |
T |
3 - 16 |
≥ 20 |
| Bending ratio (th) |
T |
2 - 16 |
≥ 1 |
| KV 0°C (J) |
L |
6 - 16 |
≥ 27 |
Prev grade
Next grade
Bending ratio: the values of the bending radius are applicable for bend angles ≤ 90º, as proposed in EN 10025-2:2004.
Chemical composition
High yield strength steels for cold forming
Full table
| |
C (%) |
Mn (%) |
P (%) |
S (%) |
Si (%) |
Al (%) |
Cu (%) |
Cr (%) |
Ni (%) |
Nb (%) |
Ceq (%) |
Galvanisation |
| Amstrong® 320MC CLAS AM FCE |
≤ 0.100 |
≤ 1.30 |
≤ 0.025 |
≤ 0.012 |
≤ 0.03 |
≥ 0.020 |
≤ 0.25 |
≤ 0.15 |
≤ 0.25 |
≤ 0.040 |
≤ 0.36 |
Class 1 |
| Amstrong® 360MC CLAS AM FCE |
≤ 0.100 |
≤ 1.40 |
≤ 0.020 |
≤ 0.012 |
≤ 0.03 |
≥ 0.020 |
≤ 0.25 |
≤ 0.15 |
≤ 0.25 |
≤ 0.065 |
≤ 0.36 |
Class 1 |
| Amstrong® 420MC CLAS AM FCE |
≤ 0.110 |
≤ 1.50 |
≤ 0.020 |
≤ 0.012 |
≤ 0.03 |
≥ 0.020 |
≤ 0.25 |
≤ 0.15 |
≤ 0.25 |
≤ 0.065 |
≤ 0.38 |
Class 1 |
| Amstrong® 500MC CLAS AM FCE |
≤ 0.120 |
≤ 1.70 |
≤ 0.020 |
≤ 0.012 |
≤ 0.03 |
≥ 0.020 |
≤ 0.25 |
≤ 0.15 |
≤ 0.25 |
≤ 0.090 |
≤ 0.42 |
Class 1 |
Amstrong® 320MC CLAS AM FCE
| |
Amstrong® 320MC CLAS AM FCE |
| C (%) |
≤ 0.100 |
| Mn (%) |
≤ 1.30 |
| P (%) |
≤ 0.025 |
| S (%) |
≤ 0.012 |
| Si (%) |
≤ 0.03 |
| Al (%) |
≥ 0.020 |
| Cu (%) |
≤ 0.25 |
| Cr (%) |
≤ 0.15 |
| Ni (%) |
≤ 0.25 |
| Nb (%) |
≤ 0.040 |
| Ceq (%) |
≤ 0.36 |
| Galvanisation |
Class 1 |
Amstrong® 360MC CLAS AM FCE
| |
Amstrong® 360MC CLAS AM FCE |
| C (%) |
≤ 0.100 |
| Mn (%) |
≤ 1.40 |
| P (%) |
≤ 0.020 |
| S (%) |
≤ 0.012 |
| Si (%) |
≤ 0.03 |
| Al (%) |
≥ 0.020 |
| Cu (%) |
≤ 0.25 |
| Cr (%) |
≤ 0.15 |
| Ni (%) |
≤ 0.25 |
| Nb (%) |
≤ 0.065 |
| Ceq (%) |
≤ 0.36 |
| Galvanisation |
Class 1 |
Amstrong® 420MC CLAS AM FCE
| |
Amstrong® 420MC CLAS AM FCE |
| C (%) |
≤ 0.110 |
| Mn (%) |
≤ 1.50 |
| P (%) |
≤ 0.020 |
| S (%) |
≤ 0.012 |
| Si (%) |
≤ 0.03 |
| Al (%) |
≥ 0.020 |
| Cu (%) |
≤ 0.25 |
| Cr (%) |
≤ 0.15 |
| Ni (%) |
≤ 0.25 |
| Nb (%) |
≤ 0.065 |
| Ceq (%) |
≤ 0.38 |
| Galvanisation |
Class 1 |
Amstrong® 500MC CLAS AM FCE
| |
Amstrong® 500MC CLAS AM FCE |
| C (%) |
≤ 0.120 |
| Mn (%) |
≤ 1.70 |
| P (%) |
≤ 0.020 |
| S (%) |
≤ 0.012 |
| Si (%) |
≤ 0.03 |
| Al (%) |
≥ 0.020 |
| Cu (%) |
≤ 0.25 |
| Cr (%) |
≤ 0.15 |
| Ni (%) |
≤ 0.25 |
| Nb (%) |
≤ 0.090 |
| Ceq (%) |
≤ 0.42 |
| Galvanisation |
Class 1 |
Prev grade
Next grade
Structural steels
Full table
| |
C (%) |
Mn (%) |
P (%) |
S (%) |
Si (%) |
Al (%) |
Cu (%) |
Cr (%) |
Ni (%) |
Nb (%) |
Ceq (%) |
Galvanisation |
| S200 CLAS AM FCE |
≤ 0.080 |
≤ 0.45 |
≤ 0.025 |
≤ 0.025 |
≤ 0.03 |
≥ 0.020 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
≤ 0.16 |
Class 1 |
| S240 CLAS AM FCE |
≤ 0.170 |
≤ 0.80 |
≤ 0.025 |
≤ 0.025 |
≤ 0.03 |
≥ 0.020 |
≤ 0.25 |
- |
- |
- |
≤ 0.35 |
Class 1 |
| S275 CLAS AM FCE |
≤ 0.180 |
≤ 1.30 |
≤ 0.025 |
≤ 0.025 |
≤ 0.03 |
≥ 0.020 |
≤ 0.25 |
≤ 0.15 |
≤ 0.25 |
- |
≤ 0.40 |
Class 1 |
| S355 CLAS AM FCE |
≤ 0.200 |
≤ 1.60 |
≤ 0.025 |
≤ 0.012 |
≤ 0.03 |
≥ 0.020 |
≤ 0.25 |
≤ 0.15 |
≤ 0.25 |
≤ 0.060 |
≤ 0.45 |
Class 1 |
S200 CLAS AM FCE
| |
S200 CLAS AM FCE |
| C (%) |
≤ 0.080 |
| Mn (%) |
≤ 0.45 |
| P (%) |
≤ 0.025 |
| S (%) |
≤ 0.025 |
| Si (%) |
≤ 0.03 |
| Al (%) |
≥ 0.020 |
| Cu (%) |
- |
| Cr (%) |
- |
| Ni (%) |
- |
| Nb (%) |
- |
| Ceq (%) |
≤ 0.16 |
| Galvanisation |
Class 1 |
S240 CLAS AM FCE
| |
S240 CLAS AM FCE |
| C (%) |
≤ 0.170 |
| Mn (%) |
≤ 0.80 |
| P (%) |
≤ 0.025 |
| S (%) |
≤ 0.025 |
| Si (%) |
≤ 0.03 |
| Al (%) |
≥ 0.020 |
| Cu (%) |
≤ 0.25 |
| Cr (%) |
- |
| Ni (%) |
- |
| Nb (%) |
- |
| Ceq (%) |
≤ 0.35 |
| Galvanisation |
Class 1 |
S275 CLAS AM FCE
| |
S275 CLAS AM FCE |
| C (%) |
≤ 0.180 |
| Mn (%) |
≤ 1.30 |
| P (%) |
≤ 0.025 |
| S (%) |
≤ 0.025 |
| Si (%) |
≤ 0.03 |
| Al (%) |
≥ 0.020 |
| Cu (%) |
≤ 0.25 |
| Cr (%) |
≤ 0.15 |
| Ni (%) |
≤ 0.25 |
| Nb (%) |
- |
| Ceq (%) |
≤ 0.40 |
| Galvanisation |
Class 1 |
S355 CLAS AM FCE
| |
S355 CLAS AM FCE |
| C (%) |
≤ 0.200 |
| Mn (%) |
≤ 1.60 |
| P (%) |
≤ 0.025 |
| S (%) |
≤ 0.012 |
| Si (%) |
≤ 0.03 |
| Al (%) |
≥ 0.020 |
| Cu (%) |
≤ 0.25 |
| Cr (%) |
≤ 0.15 |
| Ni (%) |
≤ 0.25 |
| Nb (%) |
≤ 0.060 |
| Ceq (%) |
≤ 0.45 |
| Galvanisation |
Class 1 |
Prev grade
Next grade
All details provided in the ArcelorMittal Flat Carbon Europe S.A. catalogue are for information purposes only. ArcelorMittal Flat Carbon Europe S.A. reserves the right to change its product range at any time without prior notice.
For more information on our products, visit the document centre.







 Download
Download